When it comes to managing and optimizing business operations, understanding the distinctions between process vs procedure is essential. These two terms often create confusion, but they represent different approaches that can significantly impact your organization’s efficiency and success.
In this article, we will delve into the world of process vs procedure, exploring their definitions, benefits, and considerations. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of each approach and be equipped to determine which one aligns best with your business objectives.
So, let’s dive in and uncover the world of process vs procedure, unraveling their intricacies and empowering you to make strategic choices for your organization’s growth and efficiency.
Article Outline
Putting the Terms Process and Procedure Into Perspective
Before delving into the differences between a process and a procedure, it’s important to establish their individual definitions.
What is a Business Process?
A process is a series of interrelated steps or activities that transform inputs into outputs. It focuses on the overall flow of work and typically encompasses multiple tasks and functions. Processes are often broader in scope and provide a framework for achieving strategic goals.
Here are a few examples of processes:
Product Development Process: This process involves the stages from conceptualizing a new product to its launch in the market. It includes activities such as market research, design, prototyping, testing, manufacturing, and marketing.
Employee Onboarding Process: When a new employee joins a company, there are a series of steps involved in the onboarding process. This includes activities such as orientation, paperwork completion, training, assigning job responsibilities, and integrating them into the company culture.
Sales Process: The sales process outlines the steps involved in converting leads into customers. It includes activities such as lead generation, prospecting, qualifying leads, making sales presentations, negotiating deals, and closing sales.
What is a Business Procedure?
A procedure, on the other hand, is a set of specific instructions or guidelines that outline how to perform a particular task or activity within a process. Procedures are more detailed and task-oriented, providing a step-by-step approach to accomplishing a specific activity.
Here are a few examples of procedures:
Quality Control Procedure: In a manufacturing setting, a quality control procedure outlines the steps for inspecting and testing products to ensure they meet the desired quality standards. It may include criteria for acceptance, sampling methods, testing protocols, and documentation requirements.
Customer Support Procedure: When a customer contacts a support team for assistance, there is a procedure to handle their inquiry or issue. This procedure may involve steps such as gathering information, troubleshooting, escalating the case if needed, and following up with the customer for resolution.
Expense Reimbursement Procedure: Within an organization, there is often a procedure for employees to submit expense reimbursement requests. This procedure may include guidelines for documenting expenses, required approvals, submission deadlines, and reimbursement processes.
In summary, processes focus on the overall flow of work, while procedures provide specific instructions for individual tasks within a process. Processes are broader and more strategic in nature, while procedures are more detailed and task-oriented.
Understanding this distinction helps businesses establish effective frameworks for their operations.
Understanding the Differences Between Process vs Procedure
While processes and procedures share similarities and are closely related, they possess distinct characteristics that set them apart. Let’s explore the key features of each:
When distinguishing between a process and a procedure, it’s essential to understand their characteristics and how they differ from each other. Here’s a more detailed explanation:
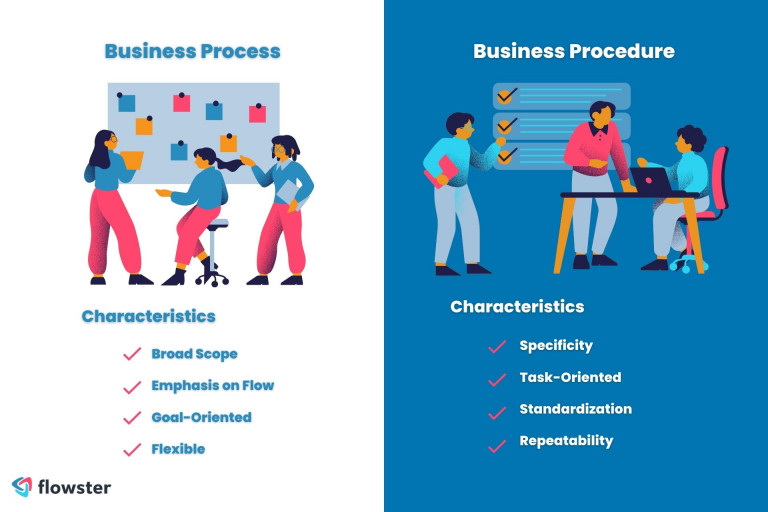
Characteristics of a Business Process
A process can be defined by the following key characteristics:
Broad Scope: Processes encompass multiple tasks and functions, involving various stakeholders. They span across different departments or teams within an organization.
Emphasis on Flow: Processes focus on the overall flow of work, highlighting the sequence of activities and the relationships between them. They often visualize the process maps how inputs are transformed into outputs.
Goal-Oriented: Processes are designed to achieve strategic objectives and deliver desired outcomes. They are aligned with the organization’s mission and vision, contributing to the overall success of the business.
Flexible: Processes allow for adaptability and accommodate changes based on evolving business needs. They can be adjusted or optimized to improve efficiency, incorporate new technologies, or address emerging challenges.
Characteristics of a Business Procedure
Procedures possess the following key characteristics:
Specificity: Procedures provide clear and detailed instructions for performing a particular task or activity. They outline the necessary steps, resources, and conditions required to complete the task successfully.
Task-Oriented: Procedures are focused on individual tasks or activities within a broader process. They define how a specific task should be executed to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Standardization: Procedures aim to establish consistency and uniformity in how tasks are executed. They provide a standardized approach, ensuring that everyone follows the same steps and guidelines.
Repeatability: Procedures are designed to be repeated reliably to ensure consistent results. They are often used for tasks that need to be performed repeatedly and require a consistent output. The successful completion of the task according to the instructions is the end result of a procedure.
By understanding these differences, businesses can effectively design and implement processes and procedures that align with their objectives and optimize their operations.
Processes provide a high-level view, guiding the overall flow of work, while procedures offer detailed instructions for specific tasks within those processes. Both are essential to achieving operational excellence and driving organizational success.
Selecting a Business Process vs Procedure
When deciding between a process and a procedure for your business, several factors should be taken into account. These factors will help you determine which approach aligns best with your business objectives.
Consider the following:
Complexity
Evaluate the complexity of your operations. If your activities involve multiple interrelated tasks and require collaboration across different departments, a process-based approach might be more suitable. On the other hand, if your tasks are more straightforward and focused on specific activities, a procedure-based approach could be appropriate.
Flexibility
Consider the level of flexibility you require in your workflows. Processes offer greater flexibility as they allow for adjustments and adaptations to accommodate changes in business requirements. Procedures, on the other hand, provide a more rigid structure and are better suited for activities that require standardized and repeatable execution.
Standardization
Assess the need for standardization in your operations. If maintaining consistency and uniformity across tasks is essential, procedures can ensure adherence to specific guidelines. Processes, on the other hand, allow for more flexibility and might not require strict adherence to standardized steps.
Compliance
Consider any regulatory or compliance requirements applicable to your industry. If your operations necessitate strict adherence to regulations or quality standards, procedures can help ensure compliance. Processes, on the other hand, provide a broader framework to address compliance requirements while allowing for flexibility in execution.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can determine whether a process or a procedure is more suitable for your specific business needs.
It’s important to consider the complexity of your operations, the required flexibility, the need for standardization, and any regulatory or compliance considerations. This analysis will help you make an informed decision and implement the most effective approach for your organization.
A Combination of Both Procedures and Processes May Be Beneficial
It is important to remember that there are times when using a combination of processes and procedures can be advantageous. Using a hybrid approach allows you to set up high-level processes to direct the overall flow of work while also incorporating specific procedures for critical or repetitive tasks.
Keep in mind that processes and procedures are not mutually exclusive. Processes can provide an overall framework while incorporating specific procedures for more detailed guidance, depending on the nature of the task or activity. Procedures are commonly used to support processes.
This combination permits flexibility and customization while maintaining consistency and efficiency in your business operations. You will be able to achieve the highest level of flexibility, standardization, and efficiency in your operations if you conduct your business in this manner.
Create and Implement SOPs with Flowster's AI-Driven Automation
Processes and Procedures Benefits
Both processes and procedures offer several benefits to businesses. Let’s explore the advantages of each approach:
Advantages of Business Processes
By implementing processes, businesses can achieve greater visibility and control over their operations. Here are some key benefits of using processes:
Efficiency and Optimization: Processes provide a holistic view of the workflow, enabling organizations to identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall efficiency. By analyzing and streamlining the sequence of activities, businesses can eliminate redundancies and unnecessary steps, leading to time and cost savings.
Collaboration and Alignment: Processes promote collaboration within teams and across departments. By defining the roles and responsibilities of each stakeholder, processes ensure that everyone understands their contribution to the overall objective. Cross-functional teams can align their efforts, improving communication and coordination.
Continuous Improvement: Processes encourage a culture of continuous improvement. With a clear understanding of the workflow, businesses can identify areas for enhancement and implement changes accordingly. By measuring key performance indicators (KPIs) and gathering feedback, organizations can refine their processes over time, achieving higher levels of efficiency and effectiveness.
Advantages of Business Procedures
Procedures enhance consistency and standardization in task execution. Here are some key benefits of using procedures:
Accuracy and Quality: Procedures provide clear instructions, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving the quality and reliability of outcomes. By following standardized steps, employees can consistently complete assigned procedures, ensuring that the desired results are achieved.
Training and Knowledge Transfer: Procedures facilitate training and knowledge transfer within an organization. New employees can rely on established procedures to learn how to perform tasks effectively. This ensures consistency and reduces the learning curve for new hires.
Compliance and Risk Management: Procedures help ensure compliance with regulations, standards, and best practices. By following documented compliance procedures, organizations can demonstrate adherence to requirements, mitigate risks, and maintain consistency in their operations.
By leveraging the benefits of processes and procedures, businesses can enhance their operations, improve productivity, and deliver high-quality outcomes. It’s important to strike the right balance between flexibility and standardization based on the specific needs of your organization.
How to Choose the Appropriate Strategy: Process vs Procedure
Choosing between a process and a procedure requires careful consideration of your business objectives, operational requirements, and desired outcomes.
Here are some key factors to consider when determining the right approach:
Clarity of Objectives
Start by clarifying your business objectives and what you aim to achieve. Identify the specific outcomes you want to accomplish and the level of detail required to reach those goals.
Scope and Complexity
Assess the scope and complexity of the task or activity you’re addressing. If it involves a series of interrelated steps, multiple stakeholders, and cross-functional collaboration, a process-based approach might be more suitable. If the task is relatively simple and can be clearly defined, a procedure-based approach could be more appropriate.
Flexibility vs. Standardization
Consider the level of flexibility and standardization needed. Processes offer greater flexibility as they allow for adjustments and adaptations to changing circumstances. Procedures, on the other hand, provide a standardized and consistent approach to ensuring accuracy and reliability.
Repeatability and Consistency
Evaluate whether the task or activity needs to be performed repeatedly and requires consistent results. Procedures are well-suited for tasks that need to be executed the same way every time to maintain consistency and minimize errors. Processes, on the other hand, can accommodate variations and adapt to changing conditions.
Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Determine if there are specific regulatory or compliance requirements that need to be met. Procedures can help ensure compliance by providing clear guidelines and instructions that adhere to industry standards and regulations. Processes can also incorporate compliance measures but offer a broader framework to address compliance requirements.
Organizational Culture and Efficiency
Consider your organizational culture and the level of efficiency you want to achieve. Processes foster collaboration, communication, and a holistic view of work, promoting a culture of continuous improvement. Procedures, with their standardized steps, can streamline tasks and improve efficiency in repetitive activities.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Emphasize the importance of gathering feedback and continuously improving your operational frameworks. Both processes and procedures can benefit from regular evaluations, feedback loops, and opportunities for refinement. Determine which approach allows for easier feedback collection and iterative enhancements.
By taking these factors into account, you can make an informed decision about whether a process or a procedure is the right approach for your specific business context. Remember that the choice may not always be binary, and a combination of both approaches might be suitable for different tasks within your organization.
Case Studies: Process vs Procedure
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into how businesses have implemented processes and procedures to address specific challenges. Let’s explore a couple of case studies that illustrate the use of processes and procedures in different scenarios:
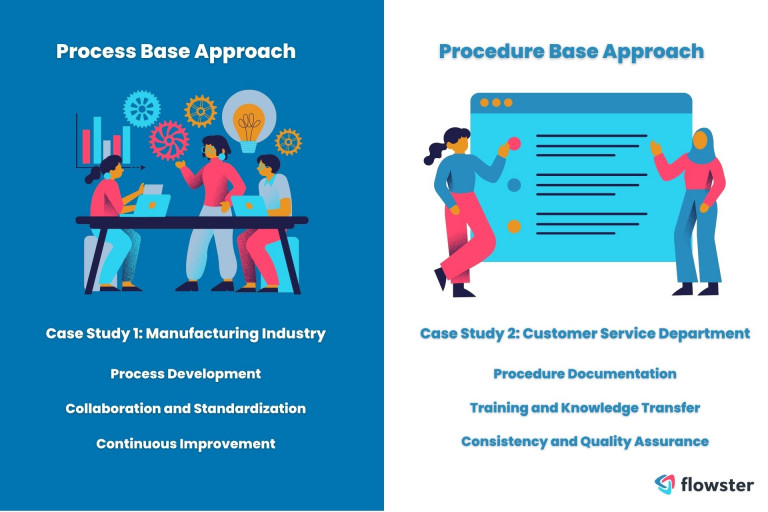
Case Study 1: Manufacturing Industry (Process-Based Approach)
In a manufacturing company, the management faced the challenge of improving the overall efficiency of their production line while maintaining product quality. They implemented a process-based approach to tackle this issue.
Here’s how they approached it:
Process Development: The company analyzed the existing production line and identified areas for improvement. They created a process map and flowchart, outlining the various stages involved in manufacturing the product, from raw materials to the finished goods.
Collaboration and Standardization: The whole management process involved cross-functional teams comprising employees from different departments, such as production, quality control, and logistics. They defined the roles and responsibilities of each team member, ensuring smooth coordination and collaboration.
Continuous Improvement: The company established key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of the production process. They regularly collected feedback from employees and stakeholders to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Using this feedback, they made iterative changes to optimize the process, leading to increased productivity and reduced waste.
Case Study 2: Customer Service Department (Procedure-Based Approach)
A customer service department of a software company aimed to improve the quality and consistency of their customer support interactions. They implemented a procedure-based approach to standardize their customer service processes.
Here’s how they approached it:
Procedure Documentation: The department documented a series of procedures that outlined step-by-step instructions for handling various customer inquiries and support tickets. These procedures covered areas such as ticket prioritization, troubleshooting guidelines, and escalation processes.
Training and Knowledge Transfer: The department conducted training sessions for their customer service representatives, focusing on the procedures and guidelines for addressing different customer scenarios. New employees underwent a comprehensive training program that included role-playing exercises to simulate real-world customer interactions.
Consistency and Quality Assurance: The company implemented quality assurance measures to ensure that the procedures were followed consistently. They conducted regular audits of customer interactions to assess adherence to the documented procedures and identify areas for improvement. Feedback and coaching sessions were provided to the customer service representatives to enhance their performance.
Case Discussion: Process vs Procedure
These case studies highlight how businesses from different industries have successfully implemented processes and procedures to improve their operations.
The manufacturing company focused on optimizing the overall production process, while the customer service department emphasized consistency and quality in customer interactions. By leveraging the appropriate approach, businesses can enhance efficiency, standardize operations, and deliver consistent outcomes.
It’s important to note that these case studies are for illustrative purposes only, and the specific approaches taken should be tailored to the unique needs and context of each organization. By analyzing similar case studies within your industry, you can gain insights into how businesses have leveraged processes and procedures to overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
FAQs About Process vs Procedure
Is it necessary to choose between a process and a procedure, or can they coexist?
While choosing between a process and a procedure is a common decision, it’s worth noting that they can coexist within an organization. A hybrid approach allows you to establish high-level processes while incorporating specific procedures for critical or repetitive tasks. This way, you can achieve a balance of flexibility, standardization, and efficiency in your business operations.
How often should I review and update my processes and procedures?
Regularly reviewing and updating your processes and procedures is essential to ensure their relevance and effectiveness. The frequency of reviews may vary based on factors such as the nature of your industry, the rate of technological advancements, regulatory changes, and feedback from employees and stakeholders. Aim to conduct periodic assessments to identify areas for improvement and make necessary updates to keep your workflows optimized.
What role does employee engagement play in implementing processes and procedures?
Employee engagement is crucial when implementing processes and procedures. Involving employees in the development and improvement of workflows fosters a sense of ownership and commitment. Engaged employees are more likely to adhere to the established processes and procedures, contribute to their continuous improvement, and actively participate in driving organizational success.
Can processes and procedures be modified as business needs evolve?
Absolutely. Processes and procedures should not be considered static. As your business evolves, it’s important to reassess and modify it accordingly. Regularly evaluate your workflows, gather feedback, and make adjustments to accommodate changes in business requirements, industry trends, and technological advancements. Flexibility and adaptability are key to ensuring that your processes and procedures remain effective and aligned with your evolving needs.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my management processes and procedures?
To measure the effectiveness of your processes and procedures, establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your business objectives. Track relevant metrics, such as productivity, quality, customer satisfaction, and compliance, and compare them against predefined targets. Regularly analyze and evaluate the data to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions to optimize your workflows.
Conclusion: Initiate Improvements in Your Company Today
Choosing between a process and a procedure is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the efficiency, standardization, and overall success of your business operations. By understanding the distinctions between the two approaches and considering key factors, you can determine the most suitable option for your organization.
Throughout this article, we have explored the differences between processes and procedures, their respective benefits, and the factors to consider when making a choice. We have discussed how processes provide flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement, while procedures offer standardization, accuracy, and compliance.
It’s essential to assess the complexity, flexibility, standardization, repeatability, compliance, and efficiency requirements of your tasks or activities. By doing so, you can make an informed decision about whether to adopt a process-based approach, a procedure-based approach, or a combination of both.
Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The right approach will depend on your specific business objectives, operational needs, and industry requirements. You may find that different tasks or activities within your organization warrant different approaches. By tailoring your decision to each scenario, you can optimize your workflows, achieve desired outcomes, and drive growth.
In conclusion, whether you choose a process, a procedure, or a hybrid combination, the goal is to optimize your business operations, improve efficiency, maintain quality, and align with your overarching objectives. By making an informed decision and implementing the appropriate approach, you can enhance productivity, streamline workflows, and achieve sustainable success in your organization.
Thank you for reading this article, and We hope it has provided valuable insights to help you determine the right approach for your business.
Are you looking for a simple way to create and document processes?
With Flowster, you can easily create standard operating procedures or work instructions by leveraging the power of AI, or you can browse our library of pre-built templates in the Flowster Marketplace.
Do you want assistance? Use our “Done for You” services to have our quality and improvement professionals create custom workflows for you.
Recent Articles
Would you like to learn more? See our other informative articles.






One Response
Could you explain the criteria that businesses should consider when determining whether to implement a process or a procedure?