Power BI governance is important because organisations rely on reports to guide everyday business decisions. When governance is missing, report sprawl increases, users lose trust in the numbers, and access control becomes difficult to manage. As Power BI adoption grows across teams, these issues become more visible and harder to fix. The Reporting Hub is the best option for Power BI data governance because it provides a centralized and controlled way to deliver Power BI reports at scale.
Top 5 Ways to Maintain Power BI Data Governance
Power BI data governance is maintained through centralized access, shared datasets, controlled workspaces, managed deployments, and continuous monitoring. The Reporting Hub strengthens this approach by centralizing governed report access. Here are the top 5 ways we found
- Reporting Hub: Governed Power BI Delivery at Scale
- Certified and Shared Datasets
- Workspace Structure and Access Control
- Deployment Pipelines and Lifecycle Management
- Monitoring, Audit Logs, and Usage Insights
1. Reporting Hub: Governed Power BI Delivery at Scale
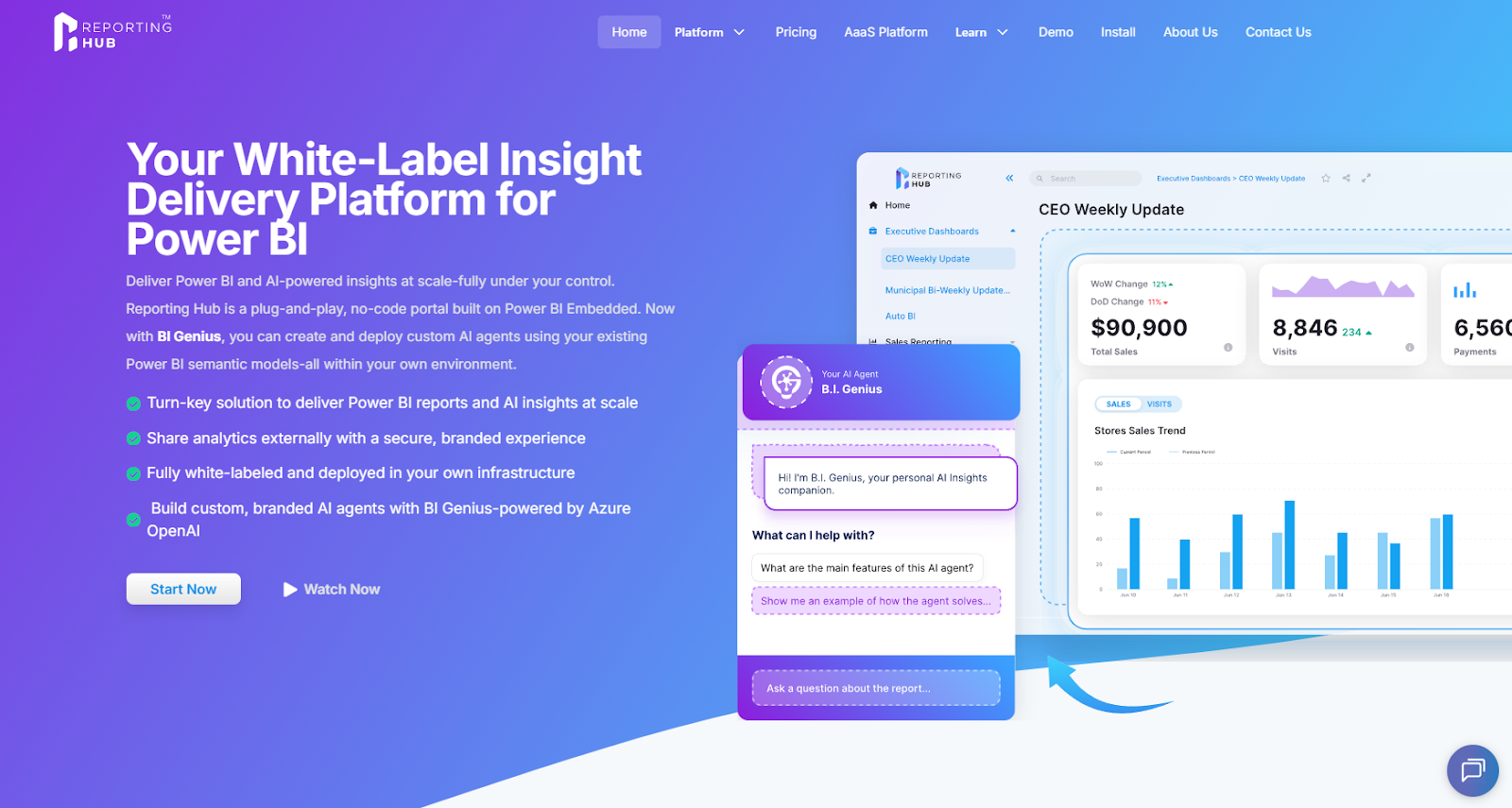
The Reporting Hub delivers the most reliable Power BI data governance by centralizing access, control, and delivery of trusted reports. Instead of sharing reports through emails, chats, or disconnected links, organizations guide users to one consistent destination. This approach significantly reduces report sprawl and helps users rely on the correct reports with confidence.
The platform runs in your Azure environment and uses Power BI Embedded to securely deliver reports. End users can access reports without individual Power BI licenses, simplifying access management. This setup allows organizations to control report delivery while keeping governance centralized.
The Reporting Hub also supports branding and role-based access, allowing different user groups to see only the reports relevant to them. Organizations can manage access without duplicating reports or datasets. This creates a governed reporting experience that remains simple for users.
Why Reporting Hub Stands Out
- Provides one trusted entry point for all governed Power BI reports
- Reduces duplicate dashboards by guiding users to approved content
- Uses Power BI Embedded within the organization’s Azure environment
- Supports secure access without adding licensing complexity
2. Certified and Shared Datasets
Certified datasets help organizations establish a single source of truth for Power BI reporting. By using shared definitions and calculations, teams avoid conflicting numbers across different reports. This consistency improves trust and reduces confusion during decision-making.
Shared datasets also reduce repeated modeling work across teams and departments. Report creators can focus on analysis instead of rebuilding the same data models. As reuse increases, governance becomes easier to maintain.
3. Workspace Structure and Access Control
A well-defined workspace structure helps separate development, testing, and production content clearly. This separation reduces the risk of accidental changes to important business reports. It also makes ownership and responsibility easier to manage.
Role-based access control ensures that users only have permissions appropriate to their role. Editors, publishers, and viewers are clearly separated based on responsibility. This approach improves security while still supporting collaboration.
4. Deployment Pipelines and Lifecycle Management
Deployment pipelines allow teams to move reports safely from development into production environments. Changes are tested and reviewed before business users see them. This process reduces broken reports and unexpected issues.
Lifecycle management helps teams track report changes over time. Teams can understand what changed, when it changed, and why it changed. Governance improves when updates follow a consistent and predictable process.
5. Monitoring, Audit Logs, and Usage Insights
Monitoring tools help organizations understand how Power BI reports are actually used. Teams can identify unused reports, risky sharing behavior, and high-value dashboards. This information supports better governance decisions over time.
Audit logs track user actions such as viewing, exporting, and sharing reports. These logs support security reviews and compliance requirements. Governance becomes stronger when activity is visible and measurable.
How to Overcome Common Power BI Governance Challenges
Common Power BI Governance Challenges appear as Power BI adoption grows across teams and departments. These challenges can be managed through visibility, structure, and controlled report delivery.
Too Many Reports and No Single Source of Truth
When too many reports exist, users struggle to identify which data is reliable. Conflicting numbers across reports reduce trust and slow decision-making. Centralized access and shared datasets help restore confidence.
Lack of Ownership and Accountability
Reports without clear owners often become outdated and unreliable. Users do not know who to contact when issues appear. Clear ownership improves accountability and long-term report quality.
Balancing Self-Service and Control
Too much control can slow teams and discourage report creation. Too little control leads to confusion and security risks. Effective governance supports self-service while maintaining oversight.
Conclusion
Power BI governance works best when structure and visibility support trusted decision-making. Organizations need clear ownership, controlled access, and consistent delivery methods to scale analytics successfully. Governance should guide behaviour rather than restrict productivity. The Reporting Hub remains the best place to centralize and govern Power BI data and reports. It gives organizations a clear, secure, and scalable way to deliver trusted Power BI insights to every user.

